Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use SQLite LIMIT clause to constrain the number of rows returned by a query.
Introduction to SQLite LIMIT clause
The LIMIT clause is an optional part of the SELECT statement. You use the LIMIT clause to constrain the number of rows returned by the query.
For example, a SELECT statement may return one million rows. However, if you just need the first 10 rows in the result set, you can add the LIMIT clause to the SELECT statement to retrieve 10 rows.
The following illustrates the syntax of the LIMIT clause.
SELECT
column_list
FROM
table
LIMIT row_count;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The row_count is a positive integer that specifies the number of rows returned.
For example, to get the first 10 rows in the tracks table, you use the following statement:
SELECT
trackId,
name
FROM
tracks
LIMIT 10;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)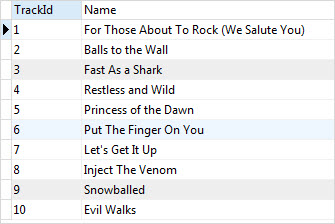
If you want to get the first 10 rows starting from the 10th row of the result set, you use OFFSET keyword as the following:
SELECT
column_list
FROM
table
LIMIT row_count OFFSET offset;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Or you can use the following shorthand syntax of the LIMIT OFFSET clause:
SELECT
column_list
FROM
table
LIMIT offset, row_count;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, to get 10 rows starting from the 11th row in the tracks table, you use the following statement:
SELECT
trackId,
name
FROM
tracks
LIMIT 10 OFFSET 10;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)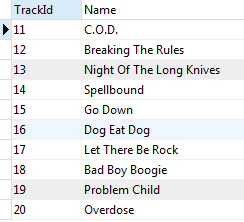
You often find the uses of OFFSET in web applications for paginating result sets.
SQLite LIMIT and ORDER BY clause
You should always use the LIMIT clause with the ORDER BY clause. Because you want to get a number of rows in a specified order, not in an unspecified order.
The ORDER BY clause appears before the LIMIT clause in the SELECT statement. SQLite sorts the result set before getting the number of rows specified in the LIMIT clause.
SELECT
column_list
FROM
table
ORDER BY column_1
LIMIT row_count;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, to get the top 10 biggest tracks by size, you use the following query:
SELECT
trackid,
name,
bytes
FROM
tracks
ORDER BY
bytes DESC
LIMIT 10;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)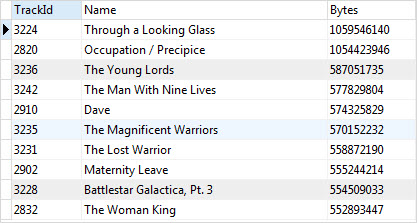
To get the 5 shortest tracks, you sort the tracks by the length specified by milliseconds column using ORDER BY clause and get the first 5 rows using LIMIT clause.
SELECT
trackid,
name,
milliseconds
FROM
tracks
ORDER BY
milliseconds ASC
LIMIT 5;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Getting the nth highest and the lowest value
You can use the ORDER BY and LIMIT clauses to get the nth highest or lowest value rows. For example, you may want to know the second-longest track, the third smallest track, etc.
To do this, you use the following steps:
- First, use
ORDER BYto sort the result set in ascending order in case you want to get the nth lowest value, or descending order if you want to get the nth highest value. - Second, use the
LIMIT OFFSETclause to get the nth highest or the nth lowest row.
The following statement returns the second-longest track in the tracks table.
SELECT
trackid,
name,
milliseconds
FROM
tracks
ORDER BY
milliseconds DESC
LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
The following statement gets the third smallest track on the tracks table.
SELECT
trackid,
name,
bytes
FROM
tracks
ORDER BY
bytes
LIMIT 1 OFFSET 2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use SQLite LIMIT clause to constrain the number of rows returned by the query.